NFS / DFS: An Overview
July 18, 2024Overview of NFS
- Developed by Sun Microsystems 1984
- Independent of operating system, network, and transport protocols.
- Available on many platforms including:
- Linux, Windows, OS/2, MVS, VMS, AIX, HP-UX….
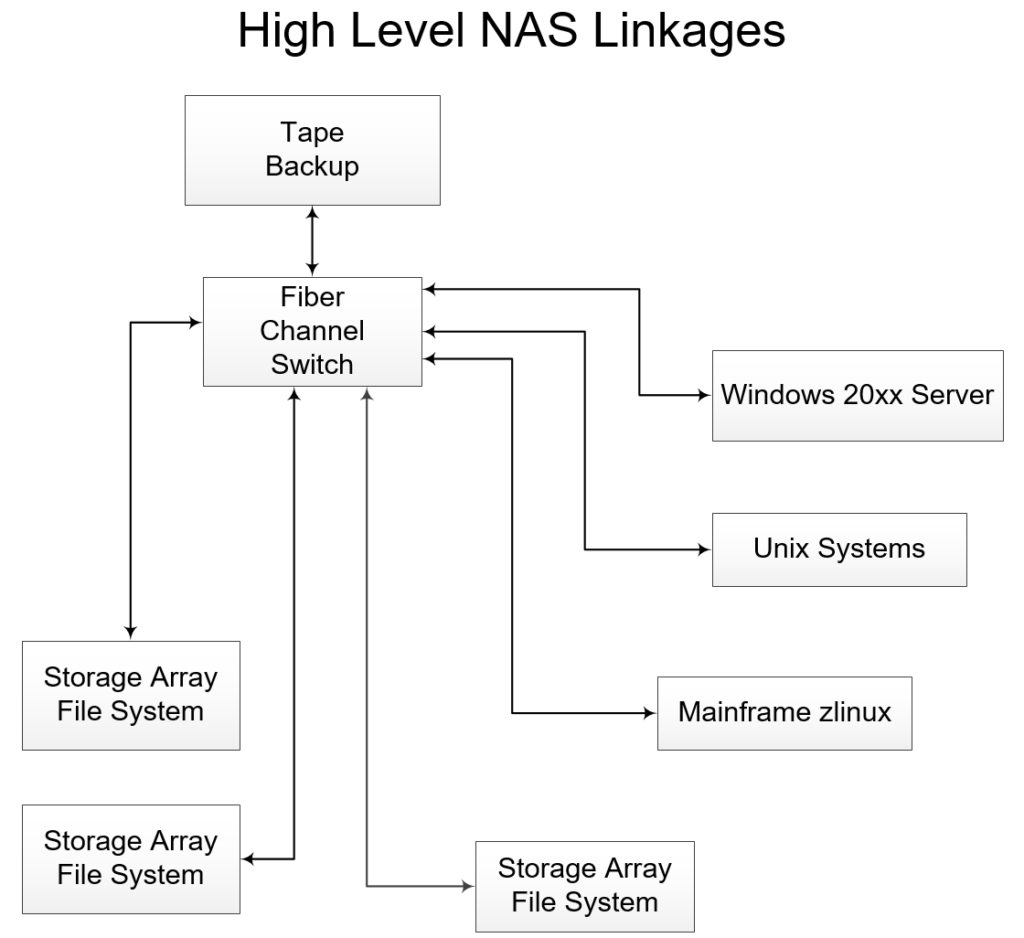
Unix distributed filesystems are used to:
- Centralize administration of disks
- Provide transparent file sharing across a network
The main systems are:
- NFS: Network File Systems developed by Sun Microsystems 1984
- AFS: Andrew Filesystem developed by Carnegie-Mellon University
Unix NFS packages usually include client and server components
- A DFS server shares local files on the network
- A DFS client mounts shared files locally
- a Unix system can be a client, server or both depending on which commands are executed
Can be fast in comparison to many other DFS
- Very little overhead
- Simple and stable protocols
- Based on RPC (The R family and S family)
Restrictions of NFS
- Stateless open architecture
- Unix filesystem semantics not guaranteed
- No access to remote special files (devices, etc.)
Restricted locking
- File locking is implemented through a separate lock daemon
- Industry standard is currently nfsV3 as default in
- RedHat, SuSE, OpenBSD, FreeBSD, Slackware, Solaris, HP-UX, Gentoo
- Kernel NFS or UserSpace NFS